钢铁工业低碳绿色发展路径与实践
绿色金融是推动经济转型升级,实现绿色低碳发展的关键路径之一 #生活知识# #生活方式# #绿色生活# #绿色金融#
摘要: 在全球进入低碳发展的新阶段的背景下,分析了不同时期的技术变革影响世界钢铁工业中心转移的历史发展趋势,提出了在全球碳中和背景下钢铁工业所面临的机遇与挑战。从国际、国内钢铁工业低碳发展现状出发,结合中国典型钢铁企业的绿色制造实践,及低碳发展规划,阐述了当前中国钢铁行业在低碳绿色发展方面所做出的探索与贡献,为钢铁企业助力国家“碳达峰、碳中和”目标的实现提供实践案例。建议未来发展路径可从四方面开展,一是在“十三五”超低排放成效的基础上向减污降碳过渡,推广烧结烟气循环及高比例球团冶炼等技术;二是实施以氢能为中心的能源结构的变革,开展多元化制氢技术,并配套加氢站网络的建设,加速绿色物流体系的构建,并在探索氢冶金技术的实践中引领行业发展;三是打造低碳绿色产业生态圈,从整个产业链、上下游协同出发,开发全生命周期评价平台及产品,并结合上下游重点企业全面推进绿色制造;四是行业突破性技术研发,加强产学研合作,整合全球创新资源。最后,在上述低碳发展路径的基础上,提出未来钢铁行业需要重视的发展建议。
关键词: 钢铁工业 / 低碳绿色 / 实践 / 路径 / 案例Abstract: Coping with climate change is a common topic facing the world. The steel industry is an important basic industry of the national economy; however, it is also a resource-intensive and typical high-carbon-emission industry. Low-carbon green is the inevitable choice and the only way for its high-quality development. Under the background that the world has entered a new stage of low-carbon development, this study analyzes the historical trend that the transfer of steel industry centers in the world is accompanied by technological change. In the new stage that China has become a steel center and will continue for a long time, it is faced with the demand for a significant reduction in carbon emissions, intensity, energy consumption, green trade barriers (such as carbon border tax), green procurement pressure, and breakthrough technology research and development challenges. This study outlines the low-carbon development plan and path of the international and domestic steel industry and focuses on the analysis of the exploration and contribution made by China’s steel industry in low-carbon green development in recent years. This study also aims to analyze the transformation of the future steel industry to low-carbon development based on the continuation of the practical achievements of green manufacturing with practical cases and summarize four types of development paths, which provide practical cases for iron and steel enterprises to help achieve the national goal of “carbon peak, carbon neutral” . The first path is to transition from ultralow-emission-centered development to pollution and carbon reduction and promote sintering flue gas circulation and high-proportion pellet smelting, selective circulation purification of sintering flue gas and waste heat utilization, and other technologies. The second path is to reform the energy structure with hydrogen energy as the center in the energy field, research and develop low-cost, large-scale hydrogen production technology, build a network of hydrogen refueling stations, accelerate the construction of green logistics systems, and lead the industry development in the practice of exploring hydrogen metallurgy technology. The third path is to rely on the cycle sustainability of steel materials (starting from the entire industrial chain and upstream and downstream coordination), utilize a full life cycle assessment platform and products, create a low-carbon green industrial ecosystem, and comprehensively promote green manufacturing in combination with upstream and downstream key enterprises. The fourth path is to conduct cooperative research and development of breakthrough technologies (such as carbon capture utilization and storage and other cutting-edge technologies) to strengthen the cooperation between industry, university, and research and integrate global innovation resources. Finally, based on the current low-carbon development trend of the steel industry and the proposed low-carbon development paths, this study analyzes the impact of international situations (such as the EU carbon border regulation mechanism on China’s steel industry), promotes the full life cycle assessment of steel materials, encourages the construction of hydrogen energy development strategies and energy source systems, establishes a green industrial chain, and recommends collaborative carbon reduction.
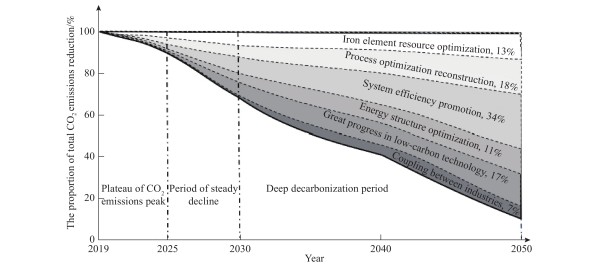
图 1 河钢集团低碳发展技术路线图
Figure 1. Technical roadmap for low-carbon development of the HBIS Group
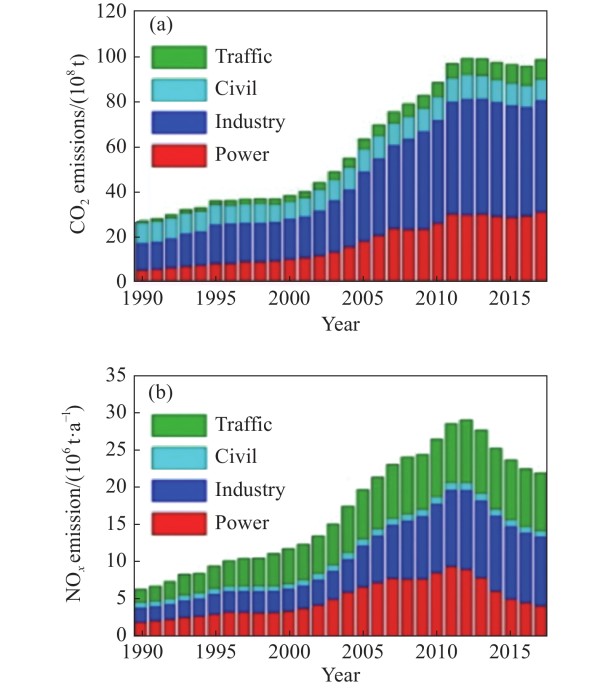
图 2 1990—2015年中国温室气体、大气污染物排放量变化趋势. (a) CO2排放量;(b)NOx排放量
Figure 2. Change trend of greenhouse gas and air pollutant emissions in China from 1990 to 2015: (a) CO2 emissions; (b) NOx emission
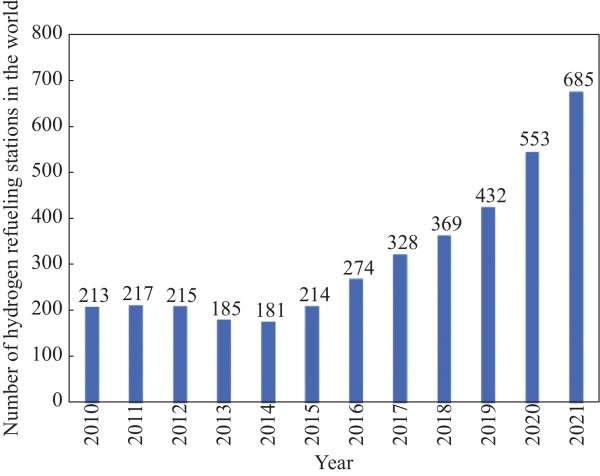
图 3 2010—2021年全球加氢站数量变化
Figure 3. Changes in the number of global hydrogen refueling stations from 2010 to 2021

图 4 “近零排放”工艺流程设计规划. (a)可再生能源制氢到氢基竖炉冶炼;(b)高效、低碳电弧炉冶炼;(c)薄板坯连铸连轧工艺
Figure 4. Flowchart of the designed “Near-zero emission” process: (a) hydrogen production from renewable energy to hydrogen-based shaft furnace smelting; (b) high-efficiency and low-carbon electric arc furnace smelting; (c) thin-slab continuous casting and rolling process
表 1 钢铁行业多工序多污染物超低排放控制技术指标
Table 1 Technical indicators of multiprocess and multipollutant ultralow emission control in the iron and steel industry
Emission standard (PM/SO2/NOx)Sintering process/ (mg·m−3)Pelletizing process/(mg·m−3)Coking process/(mg·m−3) Indicators of the HBIS Group TANGSTEEL Company10/10/405/20/308/15/60China’s ultralow emission standards10/35/5010/35/5010/30/150The most stringent standards abroad10/200/10010/200/10020/200/350 [1] 于勇. 钢铁轨迹. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2021Yu Y. Development Path of Steel Industry. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2021
[2] 李拥军, 史慧恩, 高鹏. 美国钢铁工业发展对我们的启示. 中国钢铁业, 2008(7):18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2008.07.007Li Y J, Shi H E, Gao P. Enlightenment from the development of American iron and steel industry. China Steel, 2008(7): 18 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2008.07.007
[3] 于勇. 钢铁让世界更加美好. 中国钢铁业, 2019(9):14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2019.09.007Yu Y. Steel makes the world better. China Steel, 2019(9): 14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2019.09.007
[4] 郑国栋, 陈其慎, 邢佳韵, 等. 典型国家钢铁产业发展路径与启示. 中国国土资源经济, 2021, 34(8):51Zheng G D, Chen Q S, Xing J Y, et al. The development path and enlightenment of the steel industry in typical countries. Nat Resour Econ China, 2021, 34(8): 51
[5] IEA. 钢铁技术路线图[EB/OL]. 科技论文在线(2020-10-01) [2022-10-05]. https://www.iea.org/reports/iron-and-steel-technology-roadmapIEA. Iron and steel technology roadmap [EB/OL]. Sciencepaper Online (2020-10-01) [2022-10-05]. https://www.iea.org/reports/iron-and-steel-technology-roadmap
[6] 项目综合报告编写组. 《中国长期低碳发展战略与转型路径研究》综合报告. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30(11):1Project comprehensive report preparation team. Comprehensive report on China’s long-term low-carbon development strategy and transformation path. China Popul Resour Environ, 2020, 30(11): 1
[7] 许英明, 李晓依. 欧盟碳边境调节机制对中欧贸易的影响及中国对策. 国际经济合作, 2021(5):25Xu Y M, Li X Y. Potential implications of EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism for Sino-EU trade and suggested policies for China. J Int Econ Coop, 2021(5): 25
[8] 王优酉, 张晓通, 邹磊, 等. 欧盟碳税新政: 内容、影响及应对. 国际经济合作, 2021(5):13Wang Y Y, Zhang X T, Zou L, et al. An introduction to the content and implications of EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism and proposed countermeasures for China. J Int Econ Coop, 2021(5): 13
[9] 李新创, 李晋岩, 霍咚梅, 等. 关于中国钢铁行业产品碳足迹评价标准化工作的思考. 中国冶金, 2021, 31(12):1Li X C, Li J Y, Huo D M, et al. Concerns on drafting standard for evaluating product carbon footprint of China’s steel industry. China Metall, 2021, 31(12): 1
[10] 王新东, 张弛, 孙宇佳, 等. 河钢唐钢新区绿色制造技术应用实践. 环境工程, 2022, 40(7):179 doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202207026Wang X D, Zhang C, Sun Y J, et al. Application practice of green manufacturing technology in tangsteel new district of hbis group. Environ Eng, 2022, 40(7): 179 doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.202207026
[11] 李建新, 王新东, 李双江. 河钢炼钢技术进步与展望. 炼钢, 2019, 35(4):1Li J X, Wang X D, Li S J. Progress and prospects of steelmaking technology in Hesteel. Steelmaking, 2019, 35(4): 1
[12] 王新东, 李建新, 胡启晨. 基于高炉炉料结构优化的源头减排技术及应用. 钢铁, 2019, 54(12):104Wang X D, Li J X, Hu Q C. Application practice of source and process sulfur-nitrate reduction technology based on optimization of blast furnace charge structure. Iron &Steel, 2019, 54(12): 104
[13] 王新东, 田京雷, 宋程远. 大型钢铁企业绿色制造创新实践与展望. 钢铁, 2018, 53(2):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20170533Wang X D, Tian J L, Song C Y. Innovative practice technology and outlook in large iron and steel enterprise green manufacturing. Iron &Steel, 2018, 53(2): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20170533
[14] 王新东. 以“绿色化、智能化、品牌化”为目标规划设计河钢唐钢新区. 钢铁, 2021, 56(2):12 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200554Wang X D. Planning and design of HBIS Group Tangsteel new district with goal of “Green, Intelligent and Brand”. Iron &Steel, 2021, 56(2): 12 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20200554
[15] 于勇. 品牌建设照亮高质量发展之路. 经济, 2020(8):71Yu Y. Brand building illuminates the road of high-quality development. Economy, 2020(8): 71
[16] 王新东. 河钢新发展阶段技术升级的路径与措施. 河北冶金, 2022(1):1 doi: 10.13630/j.cnki.13-1172.2022.0101Wang X D. Paths and measures of technology upgrading in the new development stage of hbis. Hebei Metall, 2022(1): 1 doi: 10.13630/j.cnki.13-1172.2022.0101
[17] 王新东, 侯长江, 田京雷. 钢铁行业烟气多污染物协同控制技术应用实践. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(9):997 doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219317Wang X D, Hou C J, Tian J L. Application and practice of multi-pollutant cooperative control technology for flue gas in iron and steel industry. Chin J Process Eng, 2020, 20(9): 997 doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219317
[18] 万芸菲, 崔阳阳, 吴雪芳, 等. 京津冀区域二氧化碳排放特征及其与大气污染物协同减排潜力分析. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 43(4):46 doi: 10.19789/j.1004-9398.2022.04.008Wan Y F, Cui Y Y, Wu X F, et al. Characteristics of carbon dioxide emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its synergistic reduction potential with air pollutants. J Cap Norm Univ (Nat Sci Ed), 2022, 43(4): 46 doi: 10.19789/j.1004-9398.2022.04.008
[19] 薛涛, 刘俊, 张强, 等. 2013—2017年中国PM2.5污染的快速改善及其健康效益. 中国科学:地球科学, 2020, 50(4):441 doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0245Xue T, Liu J, Zhang Q, et al. Rapid improvement of PM2.5 pollution and associated health benefits in China during 2013-2017. Sci Sin (Terrae), 2020, 50(4): 441 doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2019-0245
[20] 朱廷钰, 刘霄龙. 中国钢铁行业“超低排放”向“减污降碳”过渡的技术思考. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(10): 1360Zhu T Y, Liu X L. Technical considerations on the transition from "ultra-low emissions" to "pollution reduction and carbon reduction" in China's steel industry Chin J Process Eng, 2022, 22(10): 1360
[21] 车彦民, 曹莉霞, 刘金哲. 氢的大规模制备及在钢铁行业的应用和展望. 中国冶金, 2022, 32(9):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20220201Che Y M, Cao L X, Liu J Z. Large scale hydrogen production and its application and prospect in iron and steel industry. China Metall, 2022, 32(9): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20220201
[22] 鲁雄刚, 张玉文, 祝凯, 等. 氢冶金的发展历程与关键问题. 自然杂志, 2022, 44(4):251 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2022.04.001Lu X G, Zhang Y W, Zhu K, et al. Development and key problems of hydrogen metallurgy. Chin J Nat, 2022, 44(4): 251 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2022.04.001
[23] 张建良. 碳中和背景下的低碳炼铁与氢冶金. 第十三届中国钢铁年会论文集. 重庆, 2022: 49Zhang J L. Low carbon ironmaking and hydrogen metallurgy in the context of carbon neutralization // Proceedings of the 13th China Iron and Steel Annual Conference. Chongqing, 2022: 49
[24] 朱国海. 高炉富氢还原研究. 钢铁, 2020, 55(10):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190532Zhu G H. A review on hydrogen-enriched reduction in blast furnace. Iron Steel, 2020, 55(10): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20190532
[25] 王广, 王静松, 左海滨, 等. 高炉煤气循环耦合富氢对中国炼铁低碳发展的意义. 中国冶金, 2019, 29(10):1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20190107Wang G, Wang J S, Zuo H B, et al. Effect of blast furnace gas recycling with hydrogen injection on low carbon development of Chinese ironmaking. China Metall, 2019, 29(10): 1 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20190107
网址:钢铁工业低碳绿色发展路径与实践 https://www.yuejiaxmz.com/news/view/972690
相关内容
工业制造的绿色低碳发展之路:实践与探索卷烟工业企业推进绿色低碳发展的探索实践
绿色工业设计的评价体系与实践路径
工业绿色低碳发展.doc
坚持节能优先 助力工业绿色低碳和高质量发展
城市低碳转型背景下绿色交通内涵解析与发展路径
探索低碳新路径 《二次绿色装修指南》在沪发布
工业节能与绿色发展如何实现.docx
绿色出行、洁净所能 | 上海地铁的绿色低碳之路
【专家观点】坚持节能优先 助力工业绿色低碳和高质量发展

